Redux-Github
Redux-官网
Redux 中文官网
React Redux
Redux 中文文档
Redux工具包-中文文档
Redux Toolkit
七步搞定React Redux
React-Redux
「HearLing」React学习之路-redux、react-redux
学习资源
示例
Redux(基本用法)
使用Redux工具包的示例—-rtk-convert-todos-example
Redux 有很好的文档 ,还有配套的小视频(前30集 ,后30集 )
博客:React进阶(4)-拆分Redux-将store,Reducer,action,actionTypes独立管理
reducer (Function) : 接收两个参数,分别是当前的 state 树和要处理的 action ,返回新的 state 树
Reducer 必须是纯函数
不要在 reducer 中调用 API 接口请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import { createStore } from 'redux' function todos(state = [], action) { switch (action.type) { case 'ADD_TODO': return state.concat([action.text]) default: return state } } let store = createStore(todos, ['Use Redux']) store.dispatch({ type: 'ADD_TODO', text: 'Read the docs' }) console.log(store.getState()) // [ 'Use Redux', 'Read the docs' ]
小贴士#
应用中不要创建多个 store!相反,使用 combineReducers
Redux state 通常是普通 JS 对象或者数组。
如果 state 是普通对象,永远不要修改它!比如,reducer 里不要使用 Object.assign(state, newData),应该使用 Object.assign({}, state, newData)。这样才不会覆盖旧的 state。如果可以的话,也可以使用 对象拓展操作符(object spread spread operator 特性中的 return { ...state, ...newData }。
对于服务端运行的同构应用,为每一个请求创建一个 store 实例,以此让 store 相隔离。dispatch 一系列请求数据的 action 到 store 实例上,等待请求完成后再在服务端渲染应用。
当 store 创建后,Redux 会 dispatch 一个 action 到 reducer 上,来用初始的 state 来填充 store。你不需要处理这个 action。但要记住,如果第一个参数也就是传入的 state 是 undefined 的话,reducer 应该返回初始的 state 值。
要使用多个 store 增强器的时候,你可能需要使用 compose
combineReducers 辅助函数的作用是,把一个由多个不同 reducer 函数作为 value 的 object,合并成一个最终的 reducer 函数,然后就可以对这个 reducer 调用 createStore
示例 reducers/todos.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 export default function todos(state = [], action) { switch (action.type) { case 'ADD_TODO': return state.concat([action.text]) default: return state } }
reducers/counter.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 export default function counter(state = 0, action) { switch (action.type) { case 'INCREMENT': return state + 1 case 'DECREMENT': return state - 1 default: return state } }
reducers/index.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import { combineReducers } from 'redux' import todos from './todos' import counter from './counter' export default combineReducers({ todos, counter })
App.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import { createStore } from 'redux' import reducer from './reducers/index' let store = createStore(reducer) console.log(store.getState()) // { // counter: 0, // todos: [] // } store.dispatch({ type: 'ADD_TODO', text: 'Use Redux' }) console.log(store.getState()) // { // counter: 0, // todos: [ 'Use Redux' ] // }
1 2 3 4 5 6 import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' const store = configureStore({ reducer: counterReducer }) console.log(store.getState()) // {value: 0}
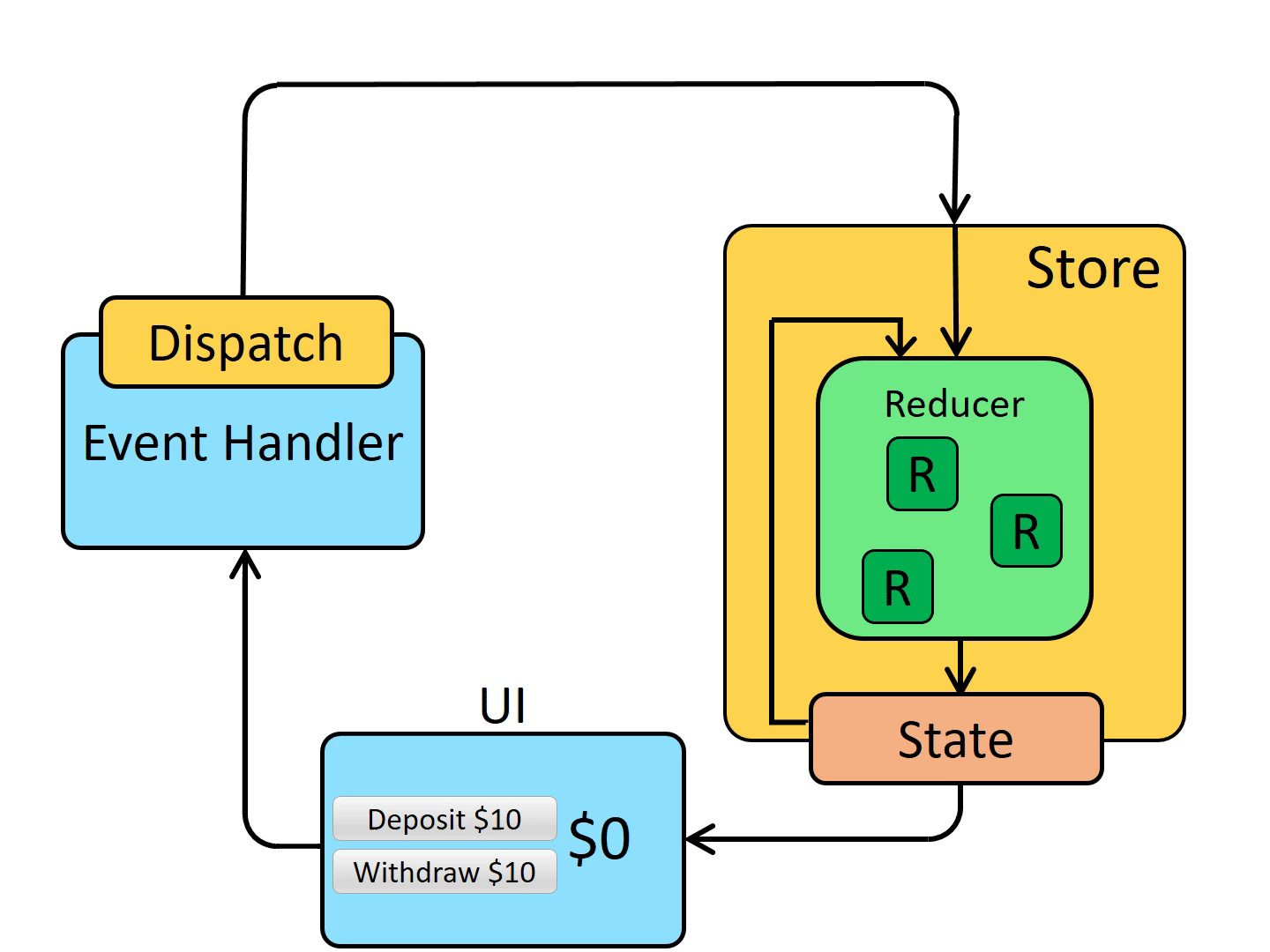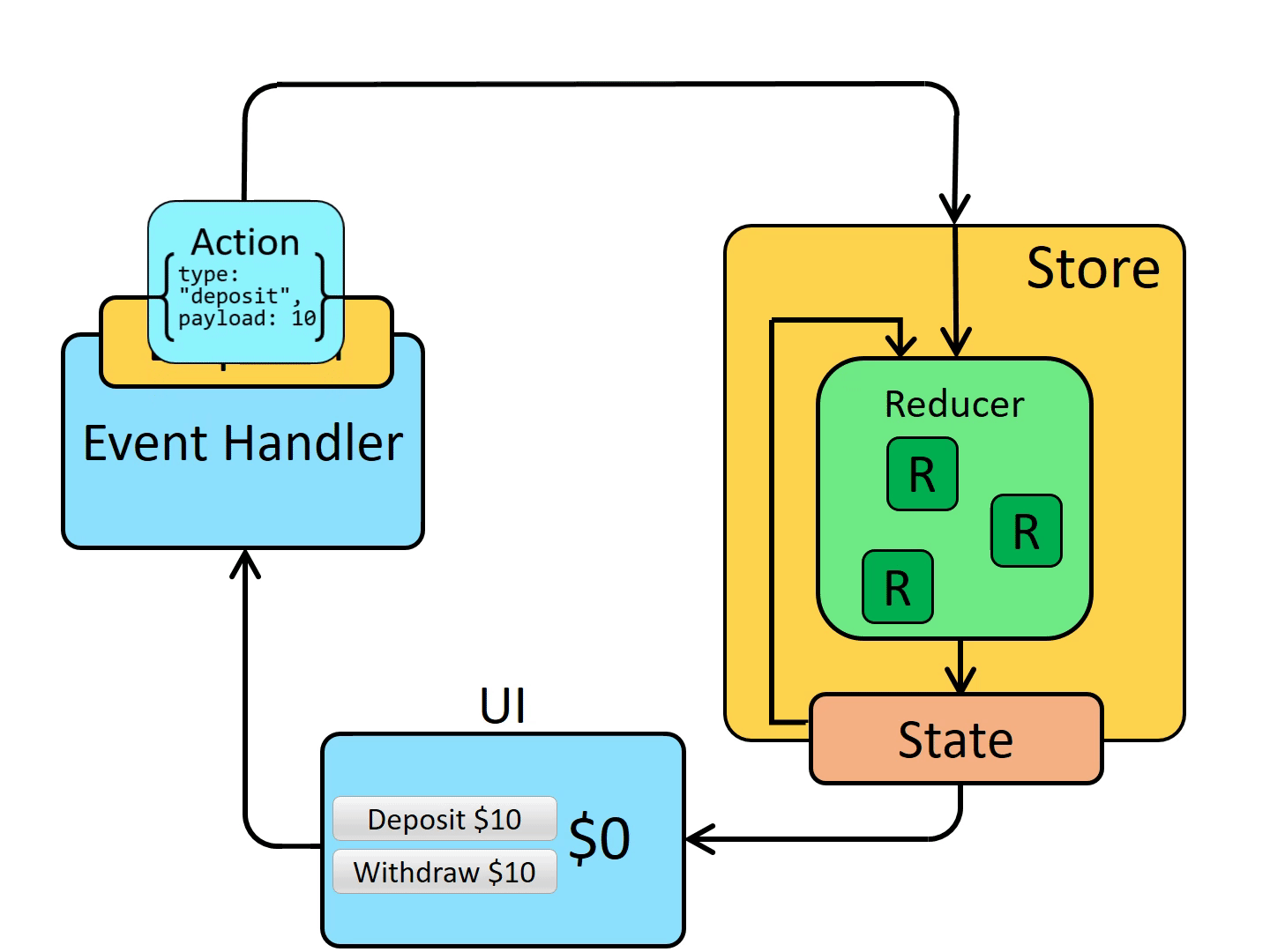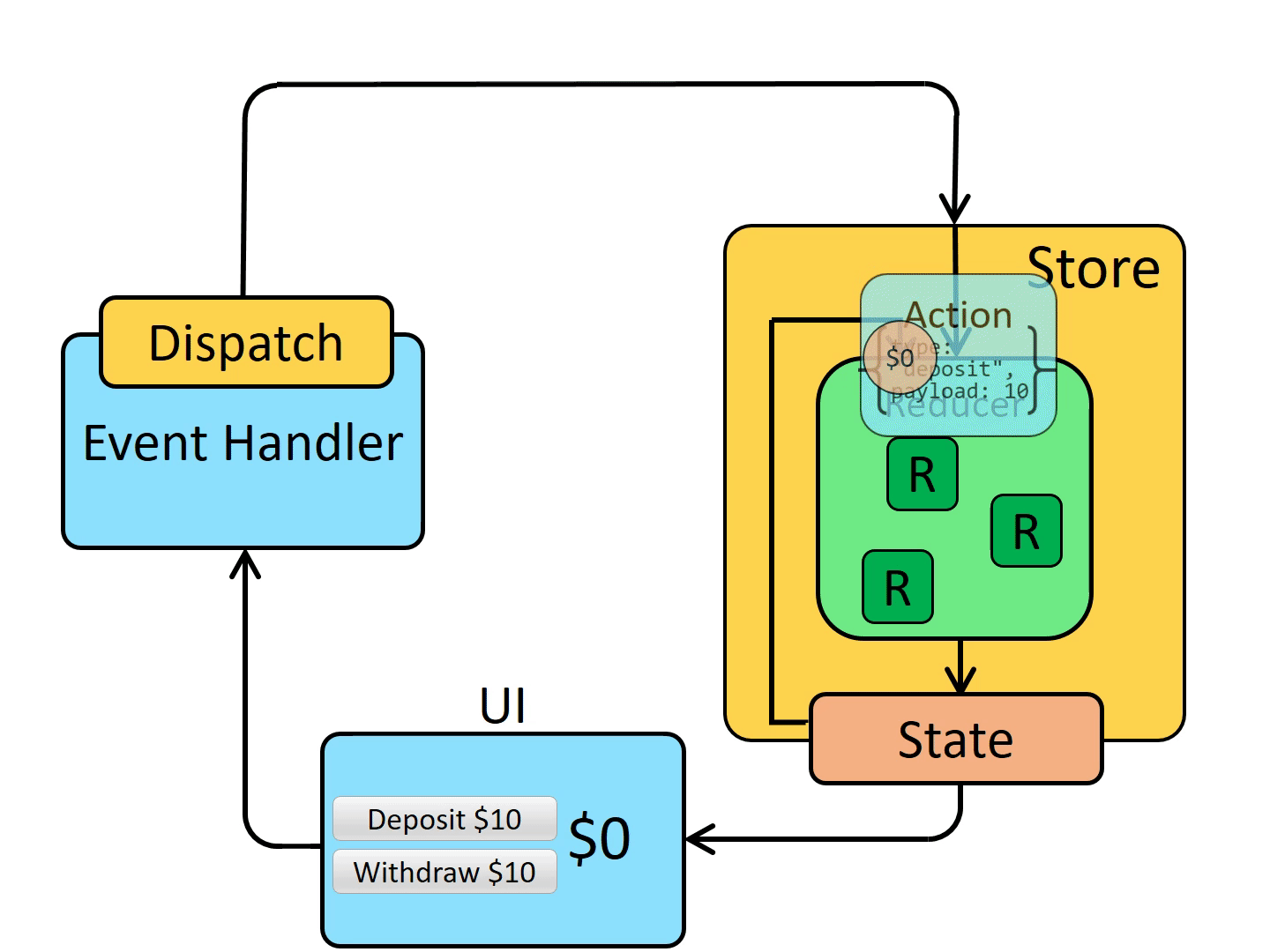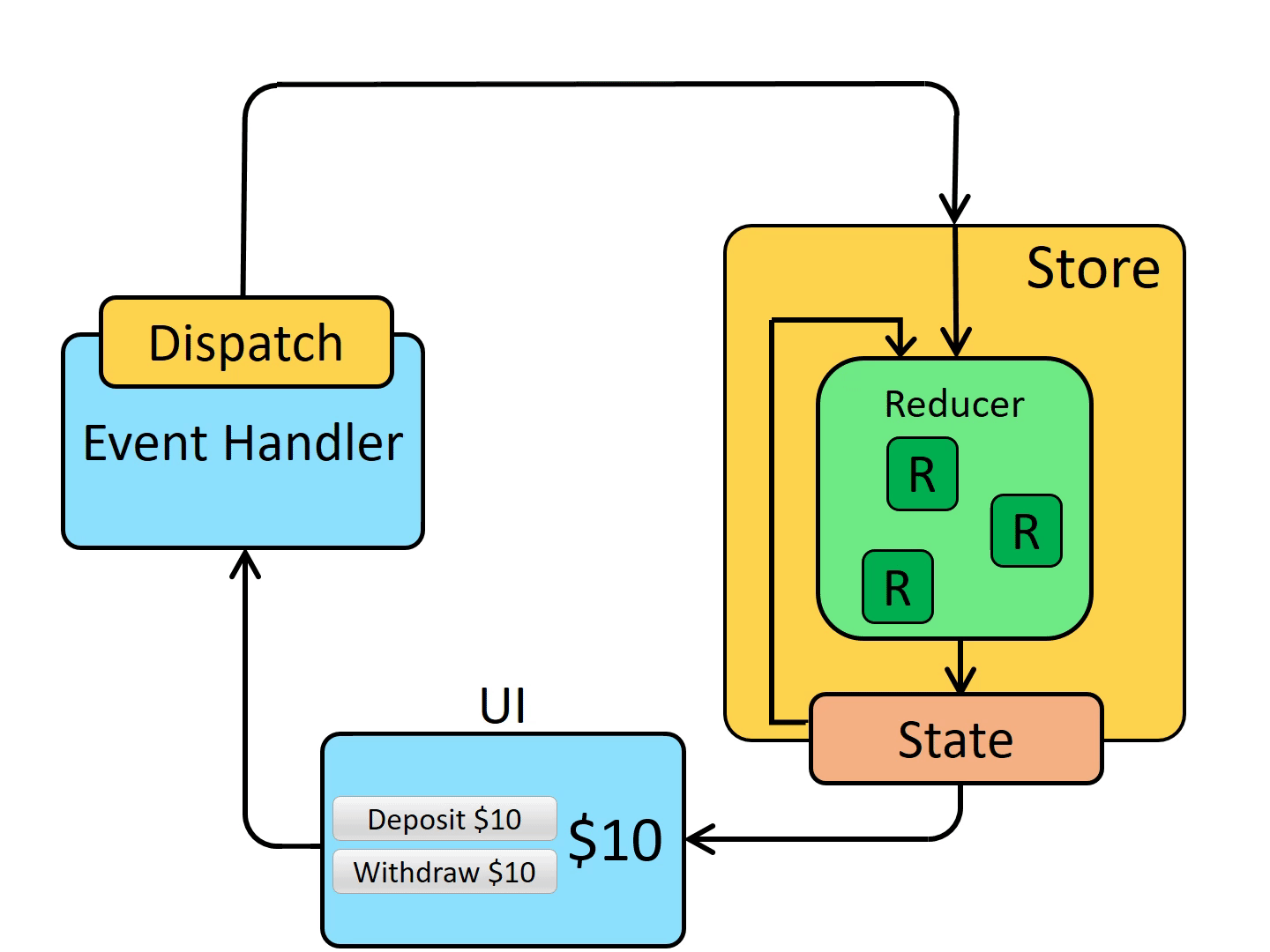
Action Action 是把数据传入 store 的惟一途径,所以任何数据,无论来自 UI 事件,网络回调或者是其它资源如 WebSockets,最终都应该以 action 的形式被 dispatch
action type 字段的普通 JavaScript 对象。你可以将 action 视为描述应用程序中发生了什么的事件 .
type 字段是一个字符串,给这个 action 一个描述性的名字,比如"todos/todoAdded"。我们通常把那个类型的字符串写成“域/事件名称”,其中第一部分是这个 action 所属的特征或类别,第二部分是发生的具体事情。
action 对象可以有其他字段,其中包含有关发生的事情的附加信息。按照惯例,我们将该信息放在名为 payload 的字段中。
1 2 3 4 const addTodoAction = { type: 'todos/todoAdded', payload: 'Buy milk' }
action creator
1 2 3 4 5 6 const addTodo = text => { return { type: 'todos/todoAdded', payload: text } }
reducer 是一个函数,接收当前的 state 和一个 action 对象,必要时决定如何更新状态,并返回新状态。函数签名是:(state, action) => newState。 你可以将 reducer 视为一个事件监听器,它根据接收到的 action(事件)类型处理事件。
禁止任何异步逻辑、依赖随机值或导致其他“副作用”的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 const initialState = { value: 0 } function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) { // 检查 reducer 是否关心这个 action if (action.type === 'counter/increment') { // 如果是,复制 `state` return { ...state, // 使用新值更新 state 副本 value: state.value + 1 } } // 返回原来的 state 不变 return state }
1 2 3 store.dispatch({ type: 'counter/increment' }) console.log(store.getState())
我们通常调用 action creator 来调用 action:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 const increment = () => { return { type: 'counter/increment' } } store.dispatch(increment()) console.log(store.getState()) // {value: 2}
初始启动:
使用最顶层的 root reducer 函数创建 Redux store
异步处理
总结
Redux 是一个管理全局应用状态的库
Redux 通常与 React-Redux 库一起使用,把 Redux 和 React 集成在一起
Redux Toolkit 是编写 Redux 逻辑的推荐方式
Redux 使用 “单向数据流”
State 描述了应用程序在某个时间点的状态,UI 基于该状态渲染
当应用程序中发生某些事情时:
UI dispatch 一个 action
store 调用 reducer,随后根据发生的事情来更新 state
store 通知 UI state 发生了变化
UI 基于新 state 重新渲染
Redux 有这几种类型的代码
Action 是有 type 字段的纯对象,描述发生了什么Reducer 是纯函数,基于先前的 state 和 action 来计算新的 state每当 dispatch 一个 action 后,store 就会调用 root reducer
redux-thunk
Writing Logic with Thunks
Middleware 是一个组合 dispatch 函数 的高阶函数,返回一个新的 dispatch 函数,通常将异步 action 转换成 action
Redux学习篇:关于store.subscribe()监听方法与取消监听的认识
Store 允许使用store.subscribe方法设置监听 函数,一旦 State 发生变化,就自动执行这个函数。
store.subscribe方法返回一个函数,调用这个函数就可以解除监听
计数器示例应用程序 本项目使用 Create-React-App 的官方 Redux 模板 创建。开箱即用,它已经配置了标准的 Redux 应用程序结构,使用 Redux Toolkit 创建 Redux 存储和逻辑,以及 React-Redux 将 Redux 存储和 React 组件连接在一起。
1 npx create-react-app redux-essentials-example --template redux
react-redux react-redux 发布了新的版本,与之前的contextAPI分离,提供对hooks的支持,那这不就更香了新的redux带来的改变
「不再需要使用」 mapStateToProps,mapDispatchToProps和connect来维护单独的container组件和UI组件,而是在组件中直接使用redux提供的hooks,读取redux中的state。可以将任何现有的自定义「hooks与redux集成」 ,而不是将通过hooks创建的state,作为参数传递给其他hooks
「useSelector:」 用于从Redux存储的state中提取值并订阅该state。
「useDispatch:」 除了读取store中的state,还能dispatch actions更新store中的state。
「useStore:」 用于获取创建的store实例
使用useSelector、useDispatch等HooksApi替代connect,减少模板代码。
useSelector accepts a single function, which we call a selector function. A selector is a function that takes the entire Redux store state as its argument, reads some value from the state, and returns that result .
1 const selectTodos = state => state.todos
1 2 3 4 const selectTotalCompletedTodos = state => { const completedTodos = state.todos.filter(todo => todo.completed) return completedTodos.length }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import React from 'react' import { useSelector } from 'react-redux' import TodoListItem from './TodoListItem' const selectTodos = state => state.todos const TodoList = () => { const todos = useSelector(selectTodos) // since `todos` is an array, we can loop over it const renderedListItems = todos.map(todo => { return <TodoListItem key={todo.id} todo={todo} /> }) return <ul className="todo-list">{renderedListItems}</ul> } export default TodoList
useSelector 自动为我们订阅了 Redux 存储! 这样,任何时候分派一个动作,它都会立即再次调用它的选择器函数。 如果选择器返回的值与上次运行时相比发生了变化,useSelector 将强制我们的组件使用新数据重新渲染。 我们所要做的就是在我们的组件中调用 useSelector() 一次,它会为我们完成剩下的工作
还值得注意的是,我们不必将选择器函数编写为单独的变量。您可以直接在 useSelector 调用中编写选择器函数
1 const todos = useSelector(state => state.todos)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 import React, { useState } from 'react' import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux' const Header = () => { const [text, setText] = useState('') const dispatch = useDispatch() const handleChange = e => setText(e.target.value) const handleKeyDown = e => { const trimmedText = e.target.value.trim() // If the user pressed the Enter key: if (e.key === 'Enter' && trimmedText) { // Dispatch the "todo added" action with this text dispatch({ type: 'todos/todoAdded', payload: trimmedText }) // And clear out the text input setText('') } } return ( <input type="text" placeholder="What needs to be done?" autoFocus={true} value={text} onChange={handleChange} onKeyDown={handleKeyDown} /> ) } export default Header
hook 是一个 JS 函数,所以它不能自动从 store.js 中自动导入 store
We do this by rendering a <Provider> component around our entire <App>, and passing the Redux store as a prop to <Provider>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom' import { Provider } from 'react-redux' import App from './App' import store from './store' ReactDOM.render( // Render a `<Provider>` around the entire `<App>`, // and pass the Redux store to as a prop <React.StrictMode> <Provider store={store}> <App /> </Provider> </React.StrictMode>, document.getElementById('root') )
React-Redux 与 React 结合使用的关键部分:
Call the useSelector hook to read data in React components
Call the useDispatch hook to dispatch actions in React components
Put <Provider store={store}> around your entire <App> component so that other components can talk to the store
在 React + Redux 应用程序中,你的全局状态应该放在 Redux 存储中,而你的本地状态应该留在 React 组件中 :
Do other parts of the application care about this data?
Do you need to be able to create further derived data based on this original data?
Is the same data being used to drive multiple components?
Is there value to you in being able to restore this state to a given point in time (ie, time travel debugging)?
Do you want to cache the data (ie, use what’s in state if it’s already there instead of re-requesting it)?
Do you want to keep this data consistent while hot-reloading UI components (which may lose their internal state when swapped)?
Most form state probably shouldn’t be kept in Redux
We can call useSelector multiple times within one component . In fact, this is actually a good idea - each call to useSelector should always return the smallest amount of state possible
简化最常见场景下的 Redux 开发,包括配置 store、定义 reducer,不可变的更新逻辑、甚至可以立即创建整个状态的 “切片 slice”,而无需手动编写任何 action creator 或者 action type。它还包括使用最广泛的 Redux 插件,例如 Redux Thunk 用于异步逻辑,而 Reselect 用于编写选择器 selector 函数,因此你可以立即使用它们。
接受一组化 reducer 函数,一个 slice 切片名和初始状态 initial state,并自动生成具有相应 action creator 和 action type 的 slice reducer
nanoid 1 2 3 import { nanoid } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' const id = nanoid()
createSlice will return an object that looks like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 { name : string, reducer : ReducerFunction, actions : Record<string, ActionCreator>, caseReducers: Record<string, CaseReducer>. getInitialState: () => State }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 { name: "todos", reducer: (state, action) => newState, actions: { addTodo: (payload) => ({type: "todos/addTodo", payload}), toggleTodo: (payload) => ({type: "todos/toggleTodo", payload}) }, caseReducers: { addTodo: (state, action) => newState, toggleTodo: (state, action) => newState, } }
reducer不容许直接修改state 1 2 3 4 5 // 对原有的上一次的state作一次深拷贝,在Redux中,reducer不容许直接修改state // const newState = Object.assign({}, state); const newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state)); newState.inputValue = action.value; // 将新的value值赋值给newState return newState;
Examples 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 import { createSlice, createAction } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' import { createStore, combineReducers } from 'redux' const incrementBy = createAction('incrementBy') const decrementBy = createAction('decrementBy') const counter = createSlice({ name: 'counter', initialState: 0, reducers: { increment: (state) => state + 1, decrement: (state) => state - 1, multiply: { reducer: (state, action) => state * action.payload, prepare: (value) => ({ payload: value || 2 }), // fallback if the payload is a falsy value }, }, // "builder callback API", recommended for TypeScript users extraReducers: (builder) => { builder.addCase(incrementBy, (state, action) => { return state + action.payload }) builder.addCase(decrementBy, (state, action) => { return state - action.payload }) }, }) const user = createSlice({ name: 'user', initialState: { name: '', age: 20 }, reducers: { setUserName: (state, action) => { state.name = action.payload // mutate the state all you want with immer }, }, // "map object API" extraReducers: { [counter.actions.increment]: ( state, action /* action will be inferred as "any", as the map notation does not contain type information */ ) => { state.age += 1 }, }, }) const reducer = combineReducers({ counter: counter.reducer, user: user.reducer, }) const store = createStore(reducer) store.dispatch(counter.actions.increment()) // -> { counter: 1, user: {name : '', age: 21} } store.dispatch(counter.actions.increment()) // -> { counter: 2, user: {name: '', age: 22} } store.dispatch(counter.actions.multiply(3)) // -> { counter: 6, user: {name: '', age: 22} } store.dispatch(counter.actions.multiply()) // -> { counter: 12, user: {name: '', age: 22} } console.log(`${counter.actions.decrement}`) // -> "counter/decrement" store.dispatch(user.actions.setUserName('eric')) // -> { counter: 12, user: { name: 'eric', age: 22} }
创建actions的原先做法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 const INCREMENT = 'counter/increment' function increment(amount) { return { type: INCREMENT, payload: amount, } } const action = increment(3) // { type: 'counter/increment', payload: 3 }
The createAction helper combines these two declarations into one. It takes an action type and returns an action creator for that type. The action creator can be called either without arguments or with a payload to be attached to the action. Also, the action creator overrides toString() so that the action type becomes its string representation.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import { createAction } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' const increment = createAction('counter/increment') let action = increment() // { type: 'counter/increment' } action = increment(3) // returns { type: 'counter/increment', payload: 3 } console.log(increment.toString()) // 'counter/increment' console.log(`The action type is: ${increment}`) // 'The action type is: counter/increment'
createAction accepts an optional second argument: a “prepare callback” that will be used to construct the payload value.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 import { createAction, nanoid } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' const addTodo = createAction('todos/add', function prepare(text) { return { payload: { text, id: nanoid(), createdAt: new Date().toISOString(), }, } }) console.log(addTodo('Write more docs')) /** * { * type: 'todos/add', * payload: { * text: 'Write more docs', * id: '4AJvwMSWEHCchcWYga3dj', * createdAt: '2019-10-03T07:53:36.581Z' * } * } **/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import { createAction, createReducer } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' const increment = createAction('counter/increment') const decrement = createAction('counter/decrement') const counterReducer = createReducer(0, (builder) => { builder.addCase(increment, (state, action) => state + action.payload) builder.addCase(decrement, (state, action) => state - action.payload) })
Parameters
actionCreator Either a plain action type string, or an action creator generated by createActionreducer The actual case reducer function.
Redux reducers are often implemented using a switch statement, with one case for every handled action type
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 const initialState = { value: 0 } function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) { switch (action.type) { case 'increment': return { ...state, value: state.value + 1 } case 'decrement': return { ...state, value: state.value - 1 } case 'incrementByAmount': return { ...state, value: state.value + action.payload } default: return state } }
With createReducer, your reducers instead look like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import { createAction, createReducer } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' const increment = createAction('counter/increment') const decrement = createAction('counter/decrement') const incrementByAmount = createAction('counter/incrementByAmount') const initialState = { value: 0 } const counterReducer = createReducer(initialState, (builder) => { builder .addCase(increment, (state, action) => { state.value++ }) .addCase(decrement, (state, action) => { state.value-- }) .addCase(incrementByAmount, (state, action) => { state.value += action.payload }) })
Parameters
initialState State | (() => State):
builderCallback (builder: Builder) => void builder.addCase(actionCreatorOrType, reducer)
Redux工具包-使用教程
Store数据-持久化 如何在React中实现全局数据的状态持久化?一篇文章让你看懂状态持久化
react-几步搞定redux-persist-持久化存储
src/app/RootReducers.js 1 2 3 4 5 6 import { combineReducers } from "@reduxjs/toolkit"; import userReducer from "../reducers/userSlice"; export default combineReducers({ user: userReducer })
src/app/store.js 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'; import { persistStore, persistReducer } from 'redux-persist'; import storage from 'redux-persist/lib/storage'; import rootReducer from './RootReducers'; const persistConfig = { key: 'root', storage } const persistedReducer = persistReducer( persistConfig, rootReducer ) export const store = configureStore({ reducer: persistedReducer, middleware: (getDefaultMiddleware) => getDefaultMiddleware({ serializableCheck: false, }), }) export const persistor = persistStore(store)
src/index.js 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import React from 'react'; import { Provider } from 'react-redux'; import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom' import './index.css'; import App from './App'; import * as serviceWorker from './serviceWorker'; import { store, persistor } from './app/store'; import { PersistGate } from "redux-persist/integration/react" import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client'; const container = document.getElementById('root'); const root = createRoot(container); root.render( <React.StrictMode> <Provider store={store}> <PersistGate loading={null} persistor={persistor}> <BrowserRouter> <App/> </BrowserRouter> </PersistGate> </Provider> </React.StrictMode> ); // If you want your app to work offline and load faster, you can change // unregister() to register() below. Note this comes with some pitfalls. // Learn more about service workers: https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA serviceWorker.unregister();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 {/* <Routes> <Route path="/" element={<Container/>} /> <Route path="/login" element={<Login />} /> <Route path="/home" element={<Home />}> <Route path="/home/:id" element={<Home />} /> </Route> */} {/* <Route path="/product" element={<Container />}> <Route path="/product/add" element={<AddProduct />} /> <Route path="/product/edit/:id" element={<EditProduct />} /> </Route> */} {/* </Routes> */}
Use with Redux-Persist